Component condition
The Component condition bar graph visualizes the current condition of critical components.
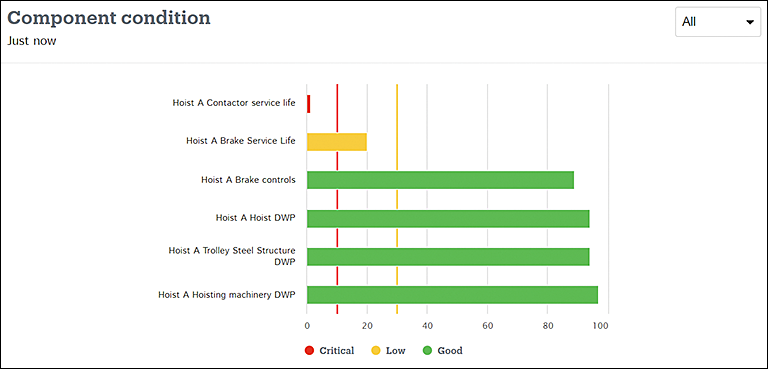
The timeframe selection does not affect this graph: The data always presents the current situation.
By default, all available components are shown. You can filter the component list with the drop-down menu top right. In multi-hoisting cases, filtering allows you to more easily spot any differences in the condition between the hoists or other components.
The colored bars present the condition of the components as DWP% (design working period). DWP% is an overall value that reflects the remaining theoretical service life of the component.
The vertical red line reflects the critical point where the DWP% falls under 10%. The yellow line marks the point for the low condition with 30% of DWP left.
The following DWP% values are typically available, depending on the type of the crane and hoist.
- Hoist DWP. Shows either the DWP% for running time (DWPRT%) or the DWP% for hoisting cycles (DWPHC%), whichever is lower. That way, the value is affected by running hours, hoisting cycles, and loads.
- Hoisting machinery DWP. Presents the DWPRT% value, which is based on the running time of the hoisting motor. Indicates the effects of running time and loads on the rotating machinery of the hoist.
- Trolley steel structure DWP. Presents the DWPHC% value, which is based on the number of hoisting cycles. Indicates the effects of hoisting cycles and loads on the steel structure of the hoist.
- Brake service life. Indicates the estimated remaining service life of the hoisting brake. Based on the number of hoisting motor starts and the number of emergency stops and abnormal stops that are issued during lifting and lowering motions.
- Brake controls. Indicates the estimated remaining service life of the hoisting brake controls.
- Contactors service life. Indicates the estimated remaining service life of the hoisting motor contactors. Based on the maximum closing count that has been specified for typical motor contactors that are used in Demag hoists. The service life of contactors is directly influenced by the usage rate of the hoist and, most significantly, whether the hoist is used in a jogging manner.´
